
Install K3s on Ubuntu 24.04 | Lightweight Kubernetes Setup
K3s is a lightweight Kubernetes distribution created by Rancher Labs, and it is highly available and production-ready. It has a small binary size and low resource requirements. In simple words, K3s is a lightweight, simplified version of Kubernetes that’s easier to install and run on smaller computers. This tutorial on PerLod Hosting will cover how to install K3s on Ubuntu 24.04 in a single-node environment. Carefully follow the instructions, and at last, you have a K3s single-node complete setup.
To try out this guide, you’ll need a Ubuntu server. If you don’t already have one, you can get a reliable VPS Hosting Service or Dedicated Server from PerLod. Our plans are optimized for Kubernetes and K3s deployments, which gives you the perfect environment to follow along with this tutorial.
Table of Contents
Why Use K3s? Use Case Examples
When you need the power of containers and Kubernetes but without complex and high resource requirements, K3s is a great choice. It is simple, light, and fast.
It can deploy and manage apps on low-power devices like Raspberry Pis in factories, retail stores, etc. K3s offers developers easily install Kubernetes on their local machines. Also, it can be useful for home labs and learning. Furthermore, K3s serves as a modern container platform for embedded systems in field appliances and is perfectly suited for CI/CD pipelines.
K3s vs Kubernetes (footprint, dependencies):
| Aspect | Kubernetes (K8s) | K3s |
| Footprint | Heavy. Requires significant CPU, RAM, and storage. | Extremely light. Single binary, ~50MB. Minimal resource usage. |
| Dependencies | Complex. Often requires multiple services and add-ons to be configured. | Simple. Bundles everything into the binary. |
Once your are understand the concept of K3s, proceed to the following steps to start a K3s single-node setup on Ubuntu 24.04.
Prerequisites
To set up K3s, you need the following requirements:
- An Ubuntu 24.04 with sudo access
- Public IP Address
- Open Ports 80 and 443 through the firewall
- A domain name points to your Public IP address
Note: By default, K3s installs Traefik as the Ingress Controller. With Traefik, K3s will start routing external terrific with ease.
At this point, prepare the Ubuntu 24.04 server for installing K3s.
Disabling Swap for K3s
First, you must disable swap on your server. To do this, run the following commands:
sudo swapoff -a
sudo sed -ri '/\sswap\s/s/^#?/#/' /etc/fstabVerify you have disabled swap by running:
free -hActivate K3s Required Kernel Modules
Next, you must enable the necessary kernel modules for installing K3s. To do this, run the following commands:
printf "overlay\nbr_netfilter\n" | sudo tee /etc/modules-load.d/k8s.conf >/dev/null
sudo modprobe overlay
sudo modprobe br_netfilterSet K3s Kernel Network Parameters
Finally, you must set up the network parameters. To do this, run the command below:
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
EOFOnce you are done, apply system configuration settings by running:
sudo sysctl --system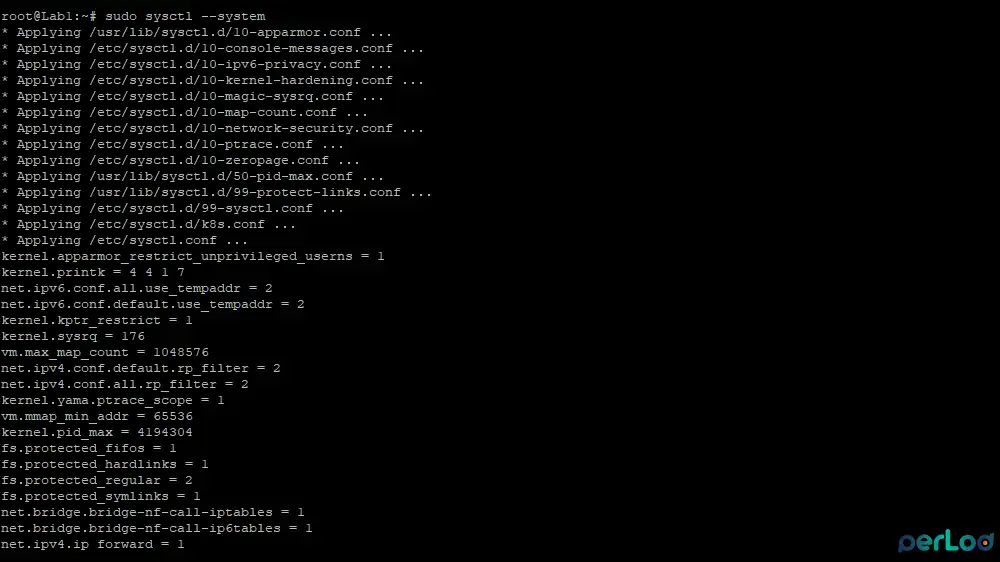
Install K3s on Ubuntu 24.04
At this point, you can start your K3s installation. Use the official installation script to install K3s on your server:
curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh -During the installation, the K3s service will be activated. Verify K3s service status with the command below:
sudo systemctl status k3s --no-pager -l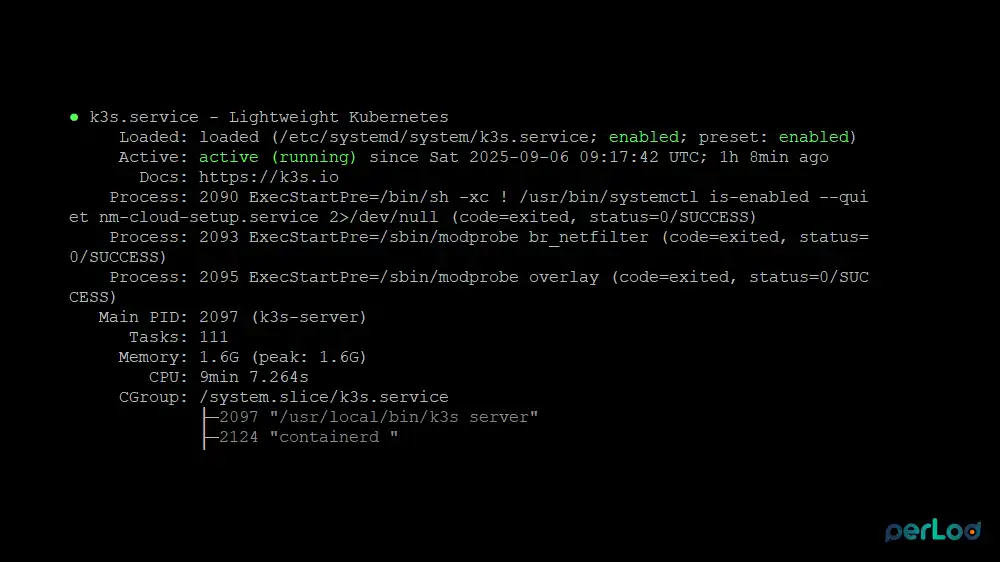
Also, check for the default nodes and pods with the following commands:
kubectl get nodes -o wide
kubectl get pods -A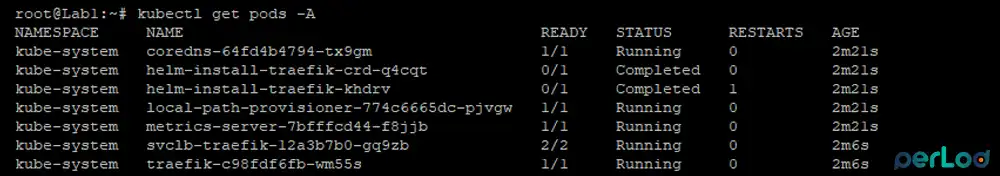
In your output, you must see a Ready node and the coredns, traefik, metrics-server, and local-path-provisioner pods running.
Now we will show you an example of deploying an Nginx test project with K3s.
Deploy Nginx with K3s – Test Project
First, create a deployment named “nginx” and tell it to run a pod using the nginx:alpine container image:
kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx:alpineThen, create a network service that displays the Nginx deployment to the outside world on a specific port, so you can access it from your browser:
kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --type=NodePortFinally, verify the details of the new “nginx” service, specifically the port number you need to use to access the website:
kubectl get svc nginxYou can test your Nginx deployment by using the curl command and the port number you got from the above command:
curl http://server-ip-address:NodePortIf you see the Welcome to nginx page, the deployment is healthy.
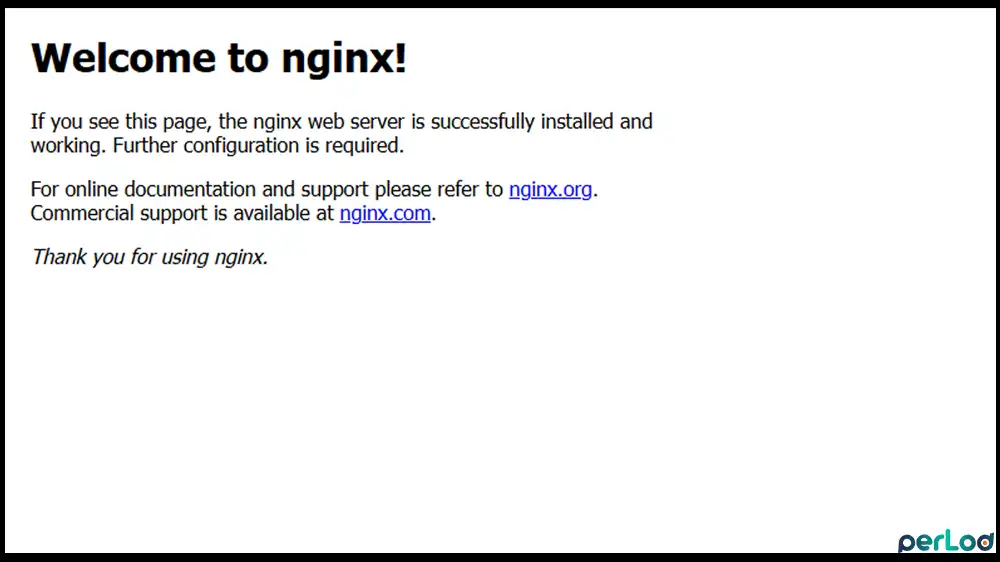
Publish Nginx on port 80 with Traefik Ingress
It is recommended to use K3s’ built-in Ingress Traefik to make your service accessible with your domain name on port 80/443.
First, create a file named nginx-ingress.yaml:
sudo nano nginx-ingress.yamlThen, add the following content to the file with your domain name. This config is a map that connects a public website address to the internal service.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress
namespace: default
spec:
ingressClassName: traefik
rules:
- host: perlod.lab.net
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx
port:
number: 80Then, run the following command to create the Ingress rule (the traffic map) defined in the nginx-ingress.yaml file:
kubectl apply -f nginx-ingress.yamlAt this point, you can test your Ingress rule so you can access the Nginx website from your browser. Use the command below:
curl http://perlod.lab.net/You should see the default Nginx welcome page. This proves that Traefik (on port 80) successfully received your request for Perlod.lab and routed it to the correct Nginx service.
Multiple domains on one service:
If you want to connect multiple domains to the same service, you can add multiple rules with different hosts within the same Ingress. For example:
spec:
ingressClassName: traefik
rules:
- host: perlod.lab1.net
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx
port:
number: 80
- host: perlod.lab2.net
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx
port:
number: 80This Ingress configuration acts as a virtual host traffic router.
Quick Troubleshooting Common K3s Errors
If service is not accessible on port 80/443, you must:
- Check your DNS record points to the correct server IP.
- Check your firewall (UFW) to ensure ports 80 and 443 are open.
- Check Traefik’s status with the following commands:
kubectl get pods -n kube-system -o wide | grep traefik
kubectl get svc -n kube-system traefikIf the Ingress rule is not working, you must:
- Ensure ingressClassName: traefik is correctly set in your Ingress YAML.
- Verify that the service name and port number in the backend section are correct.
- Check for errors using these commands:
kubectl describe ingress nginx-ingress
kubectl describe svc nginx
kubectl get events -A --sort-by=.lastTimestamp | tail -n 50Uninstalling K3s
You can clean up the resources you have created. To do this, you can run the commands below:
kubectl delete ingress nginx-ingress
kubectl delete svc nginx
kubectl delete deploy nginxThen, use the following command to completely remove the K3s software and all of its components from your server:
sudo /usr/local/bin/k3s-uninstall.shFAQs
What default components does K3s include?
K3s bundles key components such as containerd, CoreDNS, Traefik Ingress Controller, Local Path Provisioner, and a service load-balancer.
Where are K3s logs located?
Depending on the mode, it has a different location. Under the system, use journalctl -u k3s. If it runs with OpenRC, logs in /var/log/k3s.log. Pod logs in /var/log/pods, and containerd logs in /var/lib/rancher/k3s/agent/containerd/containerd.log.
How can I disable Traefik if I want to use my own Ingress?
You can start K3s with the flag: –disable=traefik. This will disable the built-in Traefik so you can deploy your own Ingress controller.
What datastore options does K3s support?
By default, K3s uses SQLite. You can also configure external datastores like MySQL, MariaDB, or PostgreSQL for HA setups.
Conclusion
In this step, you have successfully prepared your system (disabled swap, configured kernel parameters with sysctl, loaded modules), installed K3s and verified its service was running, deployed Nginx as a sample application, and it is using a Traefik Ingress on port 80.
You can now use this same structure for your real applications. You must create an internal Service and use an Ingress to publish it to the internet with different domain names.
We hope this guide (install K3s on Ubuntu 24.04) is useful for you. If you need any help, feel free and ask. Subscribe to us on X and Facebook for the latest Kubernetes updates and guides.
Further Reading:
Dedicated Servers Resurgence 2025 – why dedicated servers are becoming popular again.
Terraform and Ansible Dedicated Server Automation – step-by-step guide to automating server deployment and configuration.
