Horizontal vs Vertical Scaling in Dedicated Servers
As businesses grow and user demands increase, scalability becomes an essential concern. In this guide, we will break down the Horizontal and Vertical Scaling in Dedicated Servers. Discuss when to scale, explore the cost and technical implications, and cover essential tools and techniques such as load balancing, database replication, monitoring, and auto-scaling. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap to choose the best strategy for your infrastructure.
At PerLod Hosting, we provide dedicated server hosting solutions designed to make both horizontal and vertical scaling easier.
Table of Contents
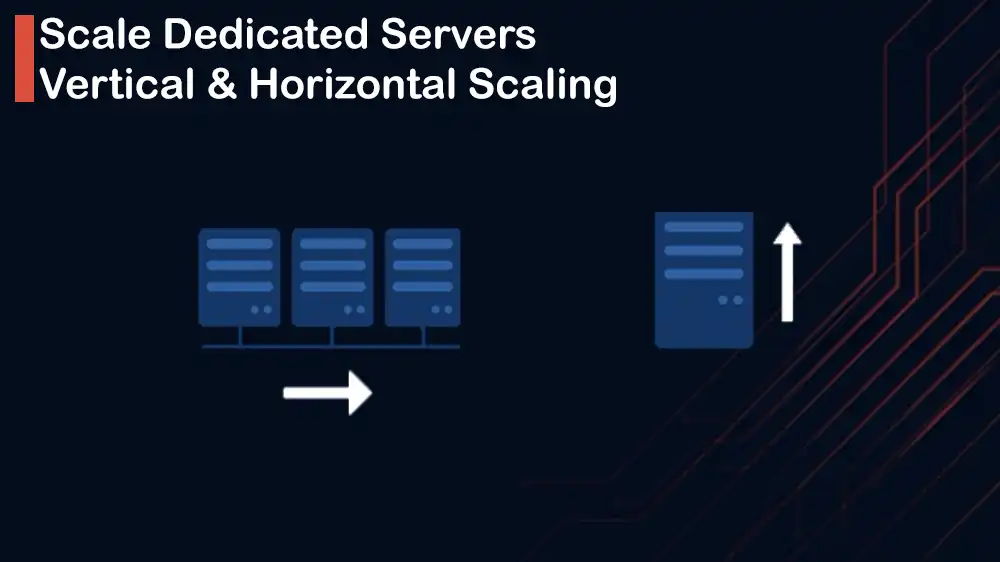
Understanding Horizontal vs Vertical Scaling in Dedicated Servers
The first step is to understand the Horizontal and Vertical scaling in dedicated servers.
Vertical Scaling (Scaling Up): If you upgrade the resources of a single server, it means you have vertical scaling. You can improve your performance by adding more CPU, increasing RAM, or upgrading storage drivers. For example, if you move from a 16-core CPU to a 64-core CPU, it is vertical scaling.
The advantages of vertical scaling include easy management because it is a single server. It doesn’t need complex configuration, and it’s best for workloads not designed to run across multiple machines. On the other hand, it has hardware limitations, potential downtime during upgrades, and if the server crashes, everything goes offline.
Horizontal Scaling (Scaling Out): If you add more servers and spread he traffic across them, it means you have horizontal scaling. It comes with unlimited scalability, increased redundancy and reliability, and it is best for distributed applications and cloud-native systems.
But you must consider that it needs high configuration, like load balancers and software that supports clustering. Also, it can cause higher costs because of the multiple servers in use.
When to Scale Dedicated Servers?
Knowing when to scale your dedicated servers is important. Scaling too early means you are paying for unused resources, while scaling too late can cause downtime, slow response times, and frustrated users. Here are the key moments when scaling becomes necessary:
Consistently High Resource Usage: If your CPU, RAM, or disk I/O is constantly above 70–80% usage for extended periods, that’s a clear signal your current server setup is under pressure. It’s time to add more resources.
Increased User Traffic: When your application or website grows fast and has high traffic, you will need to scale to handle the extra load without performance issues.
Slow Application Performance: If page loads, queries, or transactions are slowing down, your hardware may have reached its limit. At this point, scaling becomes necessary to maintain user experience.
Frequent Outages or Downtime: If your server crashes or becomes unavailable during peak traffic, scaling helps reduce downtime risks by distributing workloads.
New Feature Rollouts: With the launch of new features, you may need more computing power. Scaling will help you prevent performance bottlenecks.
Compliance and Redundancy Needs: Sometimes scaling isn’t about performance but reliability. If your industry requires high availability, scaling horizontally for redundancy ensures compliance and prevents single points of failure.
Tools for Effective Scaling Dedicated Servers
Scaling dedicated servers requires the right set of tools to manage resources, optimize performance, and maintain reliability. Here are some effective tools for scaling dedicated servers:
Containerization, like Docker or Kubernetes: Containerization with Docker or Kubernetes helps horizontal scaling to be more manageable by deploying applications across multiple servers seamlessly.
Load Balancers like HAProxy, Nginx, or AWS ELB: Load balancing is essential for distributing traffic and can be an important part of horizontal scaling setups.
Configuration Management, like Ansible and Terraform: It automates server setup and scaling operations.
Virtualization Tools like VMware or Proxmox: In vertical scaling, virtualization tools are used for optimizing server utilization.
Alongside tools like Kubernetes and HAProxy, you can also explore managed dedicated server hosting in PerLod, which is optimized for scalability and performance.
Cost Implications for Scaling Dedicated Servers
Both vertical and horizontal scaling require a financial budget.
Vertical Scaling requires high hardware specs for powerful CPUs, RAM, and SSDs, and this causes a higher cost. On the other hand, it has a low maintenance cost because it has fewer servers to manage.
In Horizontal Scaling, you have more servers, which means more licensing, networking, and monitoring costs. It has high maintenance and operational costs. Also, it has long-term cost efficiency as infrastructure grows.
Load Balancers Setup in Horizontal Scaling
In horizontal scaling, load balancing is an important task because it distributes the traffic across multiple servers and prevents any single server from being overwhelmed. Common load balancer types include hardware load balancers, software load balancers, and cloud load balancers.
- Hardware Load Balancers are physical devices that are often expensive but highly reliable.
- Software Load Balancers like HAProxy or Nginx are flexible and cost-effective.
- Cloud Load Balancers are managed solutions from AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure.
Best Practices: It is recommended to use health checks to remove unhealthy servers from rotation automatically and enable sticky sessions only if necessary. and implement SSL termination at the load balancer for efficiency.
Database Replication for Scaling Dedicated Servers
As you must know, apps rely on databases, and for scaling, you face challenges. Scaling databases vertically is limited, but horizontal scaling is a better choice.
Database scaling techniques include:
1. Master-Slave Replication: In this technique, there is one main database (master) that takes care of all writing (adding, updating, and deleting data). Other databases (called slaves/replicas) only copy the master’s data and handle reading. The advantage of this technique is that it is simple and reduces load on the main database. On the other hand, it could become a bottleneck because only one master can handle writes.
2. Multi-Master Replication: In this method, multiple servers can both read and write. They share data to stay in sync. It is more flexible and has no single point of failure. But you must consider that it is harder to keep everything consistent.
3. Sharding: Instead of copying the whole database everywhere, you split the data into smaller chunks (called shards) and spread them across different servers. Each server is responsible for only part of the data. It can handle very large amounts of data and traffic, but it is harder to manage.
Resource Monitoring for Scaling
With resource monitoring, you will know when to scale before performance decreases. You must track CPU and memory utilization, disk I/O and storage capacity, network throughput, database query performance, response times, and error rates.
Tools like Prometheus with Grafana, or Nagios will help you to monitor your resources.
Auto-Scaling Techniques for Dedicated Servers
Auto-scaling automates the process of adding or removing resources based on demand. With the right strategies, you can perform auto-scaling in dedicated servers.
Auto-scaling strategies include:
Threshold-Based Scaling: Add more servers only when usage, such as CPU or memory, goes above a set limit. For example, if your shop gets too crowded, you open another counter.
Scheduled Scaling: Add resources at specific times when you already know traffic will be high. For example, a coffee shop hires extra staff every morning because they know customers rush in before work.
Predictive Scaling: Use data and machine learning to predict traffic spikes before they happen, and scale up early. For example, the coffee shop looks at the weather, holidays, and past data. If it’s a rainy Monday morning, they know more people will come in, so they prepare extra staff in advance.
Choose How To Scale? Horizontal vs Vertical Scaling?
If you want to choose a scaling plan, Horizontal vs Vertical Scaling, you must consider your workload, budget, and the business’s growth.
Choose Scaling Vertically if:
- Your application doesn’t support a distributed architecture.
- You have newly started your business.
- You need short-term performance improvements quickly.
Choose Scaling Horizontally if:
- Your application is designed for distributed environments.
- Your business grows fast.
- You need high availability and fault tolerance.
Tip: It is recommended to start with vertical scaling and shift to horizontal scaling once your resources become insufficient.
The key to Horizontal vs Vertical Scaling is flexibility; plan your infrastructure with both strategies in mind.
FAQs
Which is cheaper? Horizontal vs Vertical Scaling?
Vertical scaling is cheaper in the short term because you’re upgrading a single server. Horizontal scaling can be more cost-effective long-term for growing applications.
Can I use both scaling horizontally and vertically together?
Yes, many organizations start with vertical scaling and add horizontal scaling later for redundancy and growth.
What is the main disadvantage of vertical scaling?
The biggest disadvantage is the physical limitation. There is only a single server.
Final Words
Horizontal and Vertical Scaling in Dedicated Servers is about your business size, budget, and app design. Vertical scaling offers simplicity with limited growth, while horizontal scaling provides limitless capacity. Nowadays, many enterprises go for a hybrid model. They start with vertical scaling and then go for horizontal scaling with load balancers, database replication, and auto-scaling strategies.
Do not forget to check PerLod for high-performance dedicated hosting.
We hope you enjoy this guide. Subscribe to our X and Facebook channels to get the latest updates and guides.
For further reading:
Multi-Cloud Hosting Trends in 2025
Explore Hybrid Hosting Trends 2025
